Immunofluorescence Assays
Creative Bioarray provides high quality and customized immunofluorescence assays to accelerate your research and drug development project.
Introduction of Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence, an effective immunostaining technique, is widely used in biological research, pharmaceutical industry and clinical application. It uses specific antibodies conjugated with fluorescent dyes to bind to specific antigens or biomolecule targets in cells or tissue samples. Fluorescence can be visualized via fluorescence microscope or confocal microscope. The power of this technique is to provide graphical and quantitative data. Commonly used fluorescent dyes include fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), Rhodamine, TRITC, cyanine dyes, and Alexa Fluor® dyes.
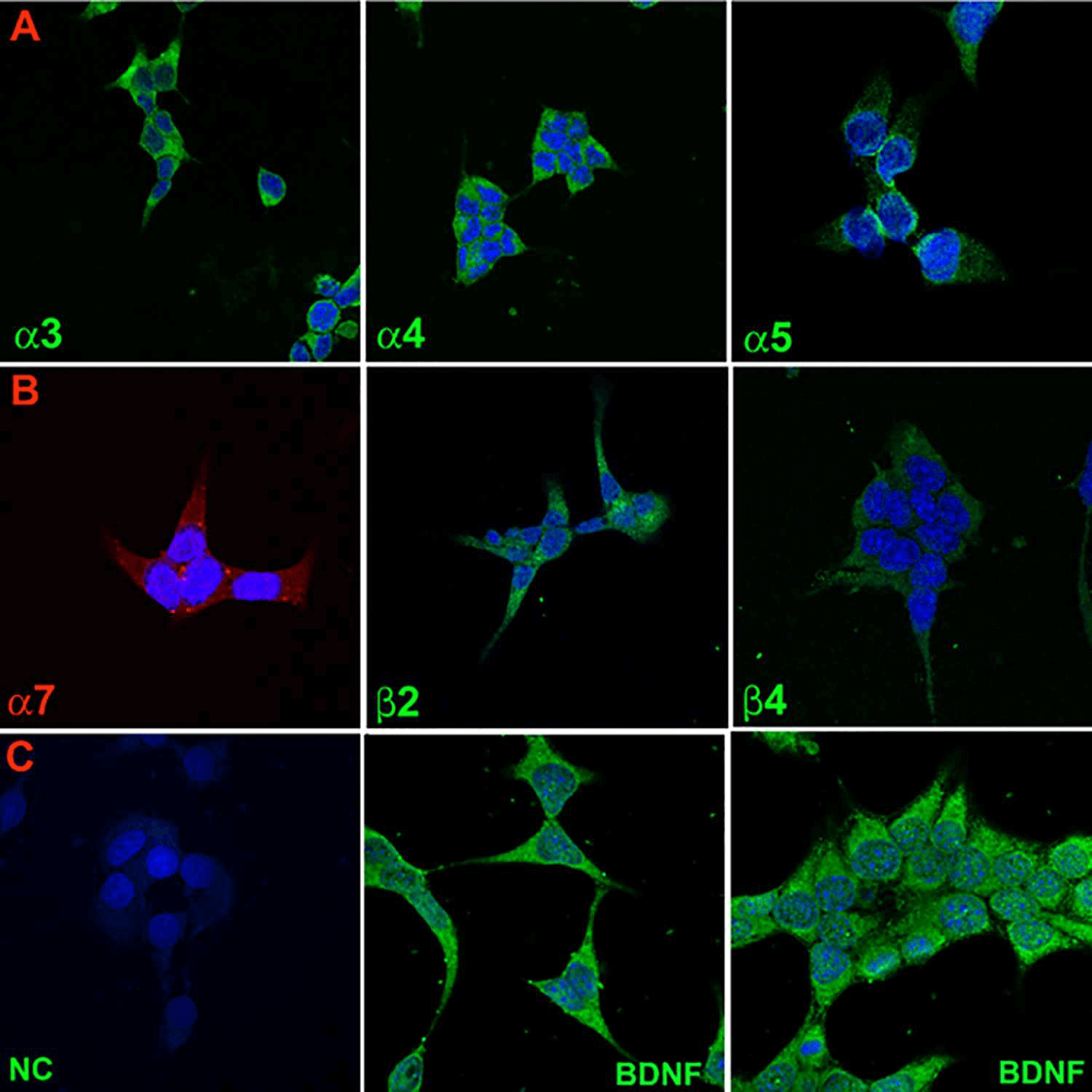
Figure 1. Immunofluorescence staining of nAChR subunits and BDNF in STC-1 cells. (Qian J, et al., 2016)
The general steps of immunofluorescence assays are sample preparation, fixation, permeabilization, blocking, antibody incubation, imaging and data collection. There are two major classes of immunofluorescence assays: direct and indirect immunofluorescence assays. The main difference is the antibody. Direct immunofluorescence uses a single antibody coupled to fluorescent dyes, while indirect immunofluorescence uses secondary antibodies coupled to fluorescent dyes to specifically bind to the unlabeled primary antibody.
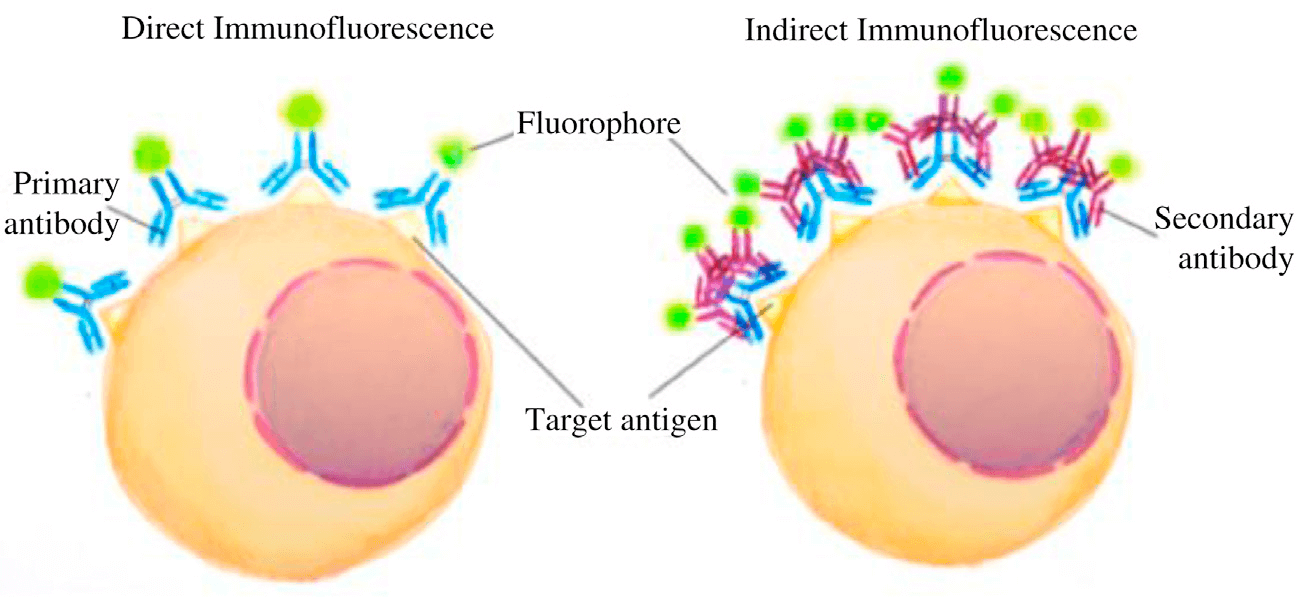
Figure 2. Direct and Indirect Immunofluorescence. (Joshi S, & Yu D., 2017)
Applications of Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is being used increasingly in various areas. The main applications are as follows:
- Determination of protein subcellular localization.
- Detection of immunoglobulins.
- Detection of humoral antibodies
- Detection of cell membrane antigens.
- Detection of cell signaling molecules.
- Visualization of cell structures.
- Detection of pathogens.
- Diagnosis of diseases.
- Used for flow cytometry.
- Detection of drugs.
Immunofluorescence Assays at Creative Bioarray
We provide different immunofluorescence assays used in adherent cells, suspension cells, individual cells, and tissue sections.
Direct Immunofluorescence Assays
Because only the primary antibody is used, the staining procedure of direct immunofluorescence assay is relatively faster and it is possible to reduce the background signal by avoiding antibody cross reactions or some problems with non-specificity. This technique is widely used for the diagnosis of diseases.
Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays
The signal amplification resulted from the increase of fluorophore molecules binding to antigens makes indirect immunofluorescence assay more sensitive. For a given primary antibody, various different secondary antibodies can be used. This provides more flexibility and possibility to simultaneously detect multiple antigens.
Anticomplement Immunofluorescence
Anticomplement immunofluorescence (ACIF) involves the binding of complement to the antigen-antibody complex. Then the anti-complement fluorescent antibody is used to specifically binding to the antigen-antibody-complement complex. This technique can be used in clinical tests.
Double and Multiple Immunofluorescent Labeling
Double or multiple immunofluorescent labeling can be used to detect the co-localization of two or more antigens in the same sample by using primary antibodies of different species in parallel or in sequence.
Creative Bioarray uses specific and well-validated antibodies to provide you meaningful and repeatable data. Our experienced scientific team can design and optimize the protocol according to the specificity of cell type and experimental purpose.
If you need more detailed information, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you.
References:
- Qian J, et al. Nicotine-induced effects on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), Ca2+ and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in STC-1 cells. PloS one, 2016, 11(11): e0166565.
- Joshi S, & Yu D. Immunofluorescence. Basic Science Methods for Clinical Researchers. Academic Press, 2017: 135-150.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.



