Immunocytochemistry Assays
Creative Bioarray provides high quality and customized immunohistochemistry assays to accelerate your research and drug development project.
Introduction of Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) is a semi-quantitative staining technique, which is commonly used to detect and visualize the distribution and localization of target peptides, proteins or antigens in cells by binding specific antibodies. Samples can be cultured cell lines, cell suspension, isolated primary cells, cytospin, aspirates, blood, and mouth swabs. The traditional technique uses chromogenic method. Enzymes conjugated with antibodies can convert chromogen substrates into a colored precipitate, thus revealing the location of the target. For horseradish peroxidase (HRP), peroxide as the substrate will appear as a brown precipitate. As technical development, the reporter linked to the antibody can be a fluorophore or gold particles, which can be visualized via a fluorescence microscope.
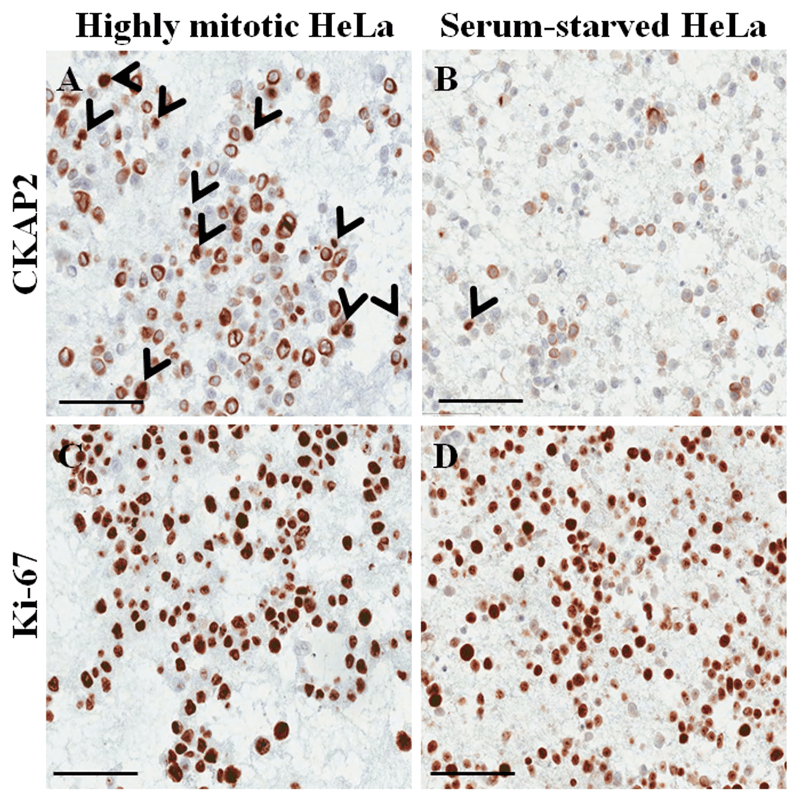
Figure 1. Immunocytochemical staining on paraffin-embedded cell block for HeLa cells. (Poojan S, et al., 2018)
The general steps of immunofluorescence assays are sample preparation on a solid support, fixation, permeabilization, blocking, antibody incubation, imaging via microscope and data collection. Similar to immunofluorescence, the methods of ICC can be divided into direct and indirect detection. The direct detection method uses one reporter-coupled antibody, while the indirect detection method uses a reporter-coupled secondary antibody, which can specifically bind to the primary antibody.
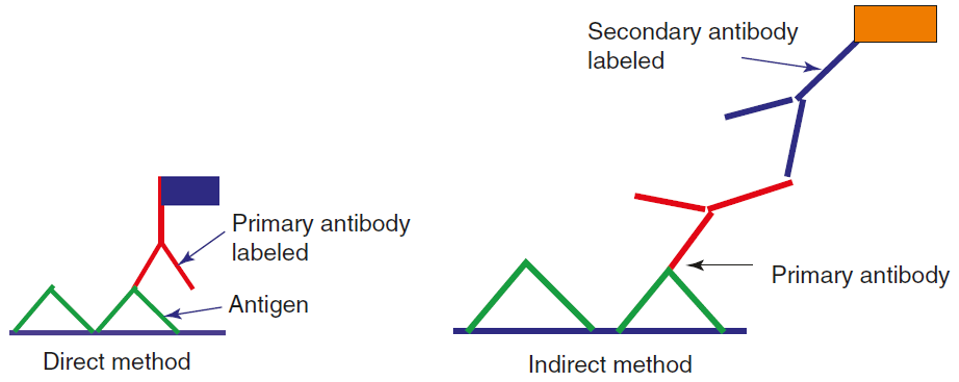
Figure 2. Scheme diagram of direct and indirect immunostaining. (Dey P., 2018)
Immunocytochemistry has been widely used in biology and pathology. The representative applications include cell apoptosis detection, determination of protein subcellular localization, disease diagnosis, and disease prognosis.
Immunocytochemistry Assays at Creative Bioarray
We provide different immunocytochemistry methods for different samples to meet specific requirements.
Direct Detection Methods
Direct detection methods are suitable to detect highly expressed antigens. The procedure is relatively simple because only one antibody conjugated to a reporter is used. This method has good flexibility.
Indirect Detection Methods
Indirect detection methods are suitable to detect poorly expressed antigens because of the signal amplification resulted from the utilization of secondary antibodies. Avidin-biotin methods can be used to further amplify the signal.
Unlabeled Antibody-Enzyme Bridge Technique
Unlabeled antibody-enzyme technique uses the secondary antibody as a bridge between the anti-enzyme antibody and the primary antibody. The enzyme can bind to anti-enzyme antibody through the principle of immunology. Peroxidase-anti-peroxidase (PAP) is the modification of this technique. These bridge techniques can avoid the damage to antibody and enzyme activity, thus improving the sensitivity.
Hapten-Sandwich Labeling
Hapten-sandwich labeling is an indirect detection method. The sandwich structure is formed by the binding of anti-hapten antibody to hapten groups, which are covalently coupled to the primary antibody binding to antigens. The advantage of this method is that the anti-hapten antibodies can be easily and efficiently purified.
Immune-Colloidal Gold Technique
Immune-colloidal gold technique is a new immunolabeling technique using colloidal gold to label the second antibody to detect antibody and antigen. This technique is widely used in immunology, histology, pathology, and cell biology.
Creative Bioarray’ immunocytochemistry assays are applicable to almost all types of cells with fast turnaround time. Our experienced scientific team can develop optimize methodologies according to the specific objectives. If you need more detailed information, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you.
References:
- Poojan S, et al. Determination of Protein Expression Level in Cultured Cells by Immunocytochemistry on Paraffin-embedded Cell Blocks. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments), 2018, 135: e57369.
- Dey P. Immunocytochemistry in Histology and Cytology. Basic and Advanced Laboratory Techniques in Histopathology and Cytology. Springer, Singapore, 2018: 149-169.
- Chivukula, M., & Dabbs, D. J. Immunocytochemistry. Comprehensive Cytopathology, 2008: 1043-1069.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.



