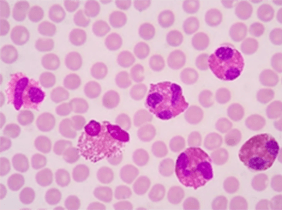
Primary cells refer to the cells that are directly isolated from living tissues. Compared with the continuous cell lines, primary cells are most closely to the tissue of origin, thus are more representative models to the in vivo state. However, they have limited life span and are more difficult to culture in vitro.
With extensive experience in isolating and culturing primary cells from various organs and tissues, we can provide customized services according to your specific needs.
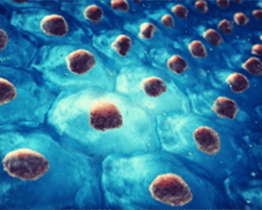
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the unique ability to develop into specialized cell types as the body needs them, and an enormous capacity for self-renewal to maintain the undifferentiated state. Stem cells can be used to study development and gene function, replace damaged cells and tissues, study the pathogenicity of diseases, and treat diseases.
We have extensive experience in isolating and culturing various kinds of stem cells from different tissues. Our expert scientists have the ability to design a customized solution to compliment your unique research needs of stem cells.
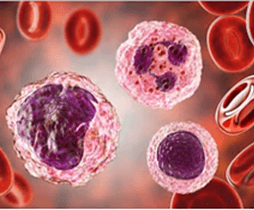
Blood cells, also known as hematopoietic cells or hematocytes, are produced through hematopoiesis and accounting for approximately 45% of the blood by volume. Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are three major components. Blood cells can be isolated from blood and used in biological assays and therapeutic applications.
We have the ability to successfully isolate and culture various types of blood cells. We have established mature protocols to provide ideal cells with fast turnaround time upon your request.
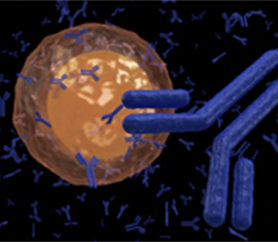
Hybridoma technology is a method used to produce large amount of monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma refers to the fusion of B lymphocyte with the capability to produce antibodies and immortal myeloma cell line. Hybridoma cells are immortalized cells with the ability to produce unlimited quantities of monoclonal antibodies with numerous applications.
We have many years of experience in culturing hybridoma cells for the production of specific antibodies. We are dedicated to providing high quality and stable hybridomas cell lines to meet your specific requirements of research or manufacturing.
There are many different immune cells (white blood cells) and other cells in the circulation and tissues, such as monocytes (monocytes and lymphocytes) or polymorphonuclear cells. Immune cell separation refers to the use of antibody-mediated recognition of specific cell surface antigens to enrich immune cell subsets, and then use flow cytometry, density centrifugation, or magnetic separation techniques for sorting or separation. In-depth and systematic research on isolated cells allows researchers to confidently answer specific research questions by minimizing interference from other cell types in the sample. The isolated cells can be used for a variety of applications, including further purification of more specific cell populations, characterization and quantification or the study of responses to various stimuli (such as pro-inflammatory cytokines). Our immune cell isolation and culture services can help you alleviate your worries.
Compared with cell lines, primary tumor cells have unparalleled advantages. For example, cancer is known for its high degree of heterogeneity. Stably passaged immortal cell lines may not be enough to represent the complexity of these diseases. Compared with stable cell lines, primary tumor cell culture constitutes a better model for simulating tumor status in vivo. This heterogeneity of the cell populations that make up the primary culture partly reproduces the tumor microenvironment and the crosstalk between malignant and healthy cells. Therefore, the isolation and culture of primary tumor cells are of great significance for studying the pathogenesis of tumors and detecting drugs. Our platform already has a mature protocol to handle the isolation and expansion of primary tumor cells. This service facilitates the isolation and culture of primary tumor cells.

Today's animal cell culture technology has become an indispensable technology in the field of life sciences, providing a foundation for the study of regulation, proliferation and differentiation, and gene manipulation. Animal cell culture has been used in various fields from basic research to advanced research. Many biotechnology products are fundamentally dependent on the large-scale cultivation of animal cell lines. The use of large-scale cultivation of animal cells to make biological products, especially proteins, is becoming more and more popular. Although rDNA has been used in bacterial cultures to produce many simpler proteins, more complex glycosylated proteins must now be produced in animal cells. At present, cell culture research aims to study the effects of culture conditions on viability, productivity, and stability of post-translational modifications, which are important for the biological activity of recombinant proteins. Our large-scale cell culture can solve the problem of excessive laboratory research and industrial production, and it is also suitable for the production of biological products within a certain capacity range.

